Suricata IPS: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Zur Navigation springen
Zur Suche springen
| Zeile 7: | Zeile 7: | ||
{{#drawio:ips}} | {{#drawio:ips}} | ||
| − | + | = Konfiguration Suricata = | |
* '''vim /etc/suricata/suricata.yml''' | * '''vim /etc/suricata/suricata.yml''' | ||
| Zeile 82: | Zeile 82: | ||
timeout: 60 | timeout: 60 | ||
default-rule-path: /etc/suricata/rules | default-rule-path: /etc/suricata/rules | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
rule-files: | rule-files: | ||
- suricata.rules | - suricata.rules | ||
| Zeile 92: | Zeile 88: | ||
reference-config-file: /etc/suricata/reference.config | reference-config-file: /etc/suricata/reference.config | ||
| − | + | = Local Rules = | |
*cat /etc/suricata/rules/local.rules | *cat /etc/suricata/rules/local.rules | ||
| Zeile 101: | Zeile 97: | ||
alert tcp any any -> any any (flags: S; msg: "SYN packet"; sid:1000000003;) | alert tcp any any -> any any (flags: S; msg: "SYN packet"; sid:1000000003;) | ||
alert udp $LAN any <> $DMZ any (msg: "DNS abfangen";) | alert udp $LAN any <> $DMZ any (msg: "DNS abfangen";) | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Firewallanpassung = | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''vim /usr/local/sbin/firewall''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | iptables -P FORWARD DROP | ||
| + | iptables -I FORWARD -i $LANDEV -o $DMZDEV -j NFQUEUE | ||
| + | ... | ||
==Start suricata== | ==Start suricata== | ||
| + | |||
*'''suricata -D -q 0 -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yml''' | *'''suricata -D -q 0 -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yml''' | ||
| − | == | + | |
| − | *iptables | + | == Problematik == |
| + | |||
| + | * Dadurch, dass Suricata alle Pakete vom LAN zur DMZ behandelt, werden alle Pakete, die nicht ausdrücklich verworfen werden akzeptiert | ||
| + | * Wir müssen Suricata also so einstellen, dass es diese Pakete wieder iptables übergibt | ||
= NFQUEUE Repeat = | = NFQUEUE Repeat = | ||
| Zeile 120: | Zeile 128: | ||
* '''vim /etc/suricata/suricata.yml''' | * '''vim /etc/suricata/suricata.yml''' | ||
| + | ... | ||
nfq: | nfq: | ||
mode: repeat | mode: repeat | ||
repeat-mark: ''1'' | repeat-mark: ''1'' | ||
repeat-mask: ''2'' | repeat-mask: ''2'' | ||
| + | ... | ||
= Links = | = Links = | ||
* https://docs.suricata.io/en/suricata-6.0.0/configuration/suricata-yaml.html#nfq | * https://docs.suricata.io/en/suricata-6.0.0/configuration/suricata-yaml.html#nfq | ||
Version vom 8. August 2023, 23:33 Uhr
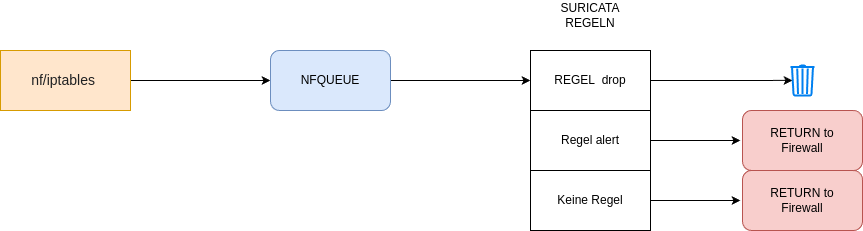
IPS
- Wir können mit iptables Pakete abfangen und einer QUEUE übergeben
- Diese QUEUE wird von suricata gelesen und ihrem REGELWERK übergeben.
- Wenn das Paket mit einer Regel übereinstimmt, wird eine Aktion ausgelöst.
- Alert führt zu einer Meldung
- Bei Drop wird das Paket verworfen.
Konfiguration Suricata
- vim /etc/suricata/suricata.yml
%YAML 1.1
---
vars:
address-groups:
LAN: "[172.16.100.0/24]"
DMZ: "[10.0.100.0/24]"
INTERNAL: "[$LAN,$DMZ]"
EXTERNAL_NET: "!$INTERNAL"
default-log-dir: /var/log/suricata/
stats:
enabled: yes
interval: 8
outputs:
- fast:
enabled: yes
filename: fast.log
append: yes
- alert-debug:
enabled: yes
filename: alert-debug.log
append: yes
- stats:
enabled: yes
filename: stats.log
append: yes # append to file (yes) or overwrite it (no)
totals: yes # stats for all threads merged together
threads: no # per thread stats
logging:
default-log-level: notice
outputs:
- console:
enabled: yes
- file:
enabled: yes
level: info
filename: suricata.log
# type: json
af-packet:
- interface: enp0s3
threads: auto
cluster-id: 99
cluster-type: cluster_flow
defrag: yes
- interface: enp0s8
threads: auto
cluster-id: 99
cluster-type: cluster_flow
defrag: yes
- interface: enp0s9
threads: auto
cluster-id: 99
cluster-type: cluster_flow
defrag: yes
pid-file: /var/run/suricata.pid
coredump:
max-dump: unlimited
host-mode: auto
unix-command:
enabled: yes
filename: /var/run/suricata-command.socket
engine-analysis:
rules-fast-pattern: yes
rules: yes
defrag:
memcap: 32mb
hash-size: 65536
trackers: 65535 # number of defragmented flows to follow
max-frags: 65535 # number of fragments to keep (higher than trackers)
prealloc: yes
timeout: 60
default-rule-path: /etc/suricata/rules
rule-files:
- suricata.rules
- local.rules
classification-file: /etc/suricata/classification.config
reference-config-file: /etc/suricata/reference.config
Local Rules
- cat /etc/suricata/rules/local.rules
drop icmp $LAN any <> $DMZ any (msg: "Ping zwischen LAN und DMZ"; sid:1000000001;) drop dns $LAN any -> $DMZ any (msg:"Kein Googlen"; dns.query; content:"google"; nocase; sid:5;) alert icmp $INTERNAL any -> !$INTERNAL any (msg:"ICMP TEST"; sid:1000000002;) alert tcp any any -> any any (flags: S; msg: "SYN packet"; sid:1000000003;) alert udp $LAN any <> $DMZ any (msg: "DNS abfangen";)
Firewallanpassung
- vim /usr/local/sbin/firewall
iptables -P FORWARD DROP iptables -I FORWARD -i $LANDEV -o $DMZDEV -j NFQUEUE ...
Start suricata
- suricata -D -q 0 -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yml
Problematik
- Dadurch, dass Suricata alle Pakete vom LAN zur DMZ behandelt, werden alle Pakete, die nicht ausdrücklich verworfen werden akzeptiert
- Wir müssen Suricata also so einstellen, dass es diese Pakete wieder iptables übergibt
NFQUEUE Repeat
- Damit Suricata die nicht gedroppten Pakete automatisch akzeptiert, sondern dies der Firewall überlässt, kann es diese Pakete markieren und zurück zu iptables schicken
- Markierungen folgen der Syntax $MARK/$MASK
- vim /usr/local/sbin/firewall
iptables -P FORWARD DROP iptables -I FORWARD -i $LANDEV -o $DMZDEV -m mark ! --mark 1/2 -j NFQUEUE iptables -A FORWARD -i $LANDEV -o $DMZDEV -j LOG --log-prefix "iptables nach Suricata!" ...
- vim /etc/suricata/suricata.yml
... nfq: mode: repeat repeat-mark: 1 repeat-mask: 2 ...