Rspamd Einrichten: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Zur Navigation springen
Zur Suche springen
(Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „=Rspamd und ClamAV installieren= ==Debian/Ubuntu== * apt install rspamd clamav-daemon clamav-freshclam redis ==RHEL/CentOS== * dnf install rspamd clamav…“) |
|||
| (33 dazwischenliegende Versionen desselben Benutzers werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 10: | Zeile 10: | ||
*systemctl enable redis.service | *systemctl enable redis.service | ||
=Läuft alles= | =Läuft alles= | ||
| − | *systemctl status | + | *systemctl status rspamd |
*systemctl status clamav-daemon | *systemctl status clamav-daemon | ||
*systemctl status redis | *systemctl status redis | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Dienste und Ports von Rspamd= | ||
| + | ==Rspamd Proxy== | ||
| + | *Der Rspamd Proxy dient als Eingangsfilter für E-Mails und leitet sie an die entsprechenden Worker weiter, um die Last zu verteilen. | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | Port: 11332/tcp (Standardport für Proxy-Dienste) | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | ==Rspamd Worker== | ||
| + | *Der Rspamd Worker führt die eigentliche Spam-Analyse durch und verarbeitet eingehende Nachrichten anhand von Regeln, Statistiken und externen Diensten. | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | Port: 11333/tcp (Standardport für Worker-Dienste) | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | ==Rspamd Controller== | ||
| + | *Der Rspamd Controller stellt eine API für Konfiguration, Statistiken und manuelles Training des Filters zur Verfügung. | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | Port: 11334/tcp (Standardport für den Controller) | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | =Passwort für den Rspamd Controller und Port nach aussen öffen= | ||
| + | ;Passwort erzeugen | ||
| + | *rspamadm pw | ||
| + | Enter passphrase: | ||
| + | $2$mqbbp8yb4fz8febgpxk7rb4db9p5njwg$xior3gxjbuc76bhsq4rapq7x98cssrm9qkr49kwapgdsahmpzjny | ||
| + | ;In der Worker Datei eintragen | ||
| + | ;Port an allen Interfaces lauschen lassen | ||
| + | *cat /etc/rspamd/override.d/worker-controller.inc | ||
| + | password = "$2$mqbbp8yb4fz8febgpxk7rb4db9p5njwg$xior3gxjbuc76bhsq4rapq7x98cssrm9qkr49kwapgdsahmpzjny"; | ||
| + | bind_socket ="*:11334"; | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Restart= | ||
| + | *systemctl restart rspamd | ||
| + | =Zugriff auf das Webinterface= | ||
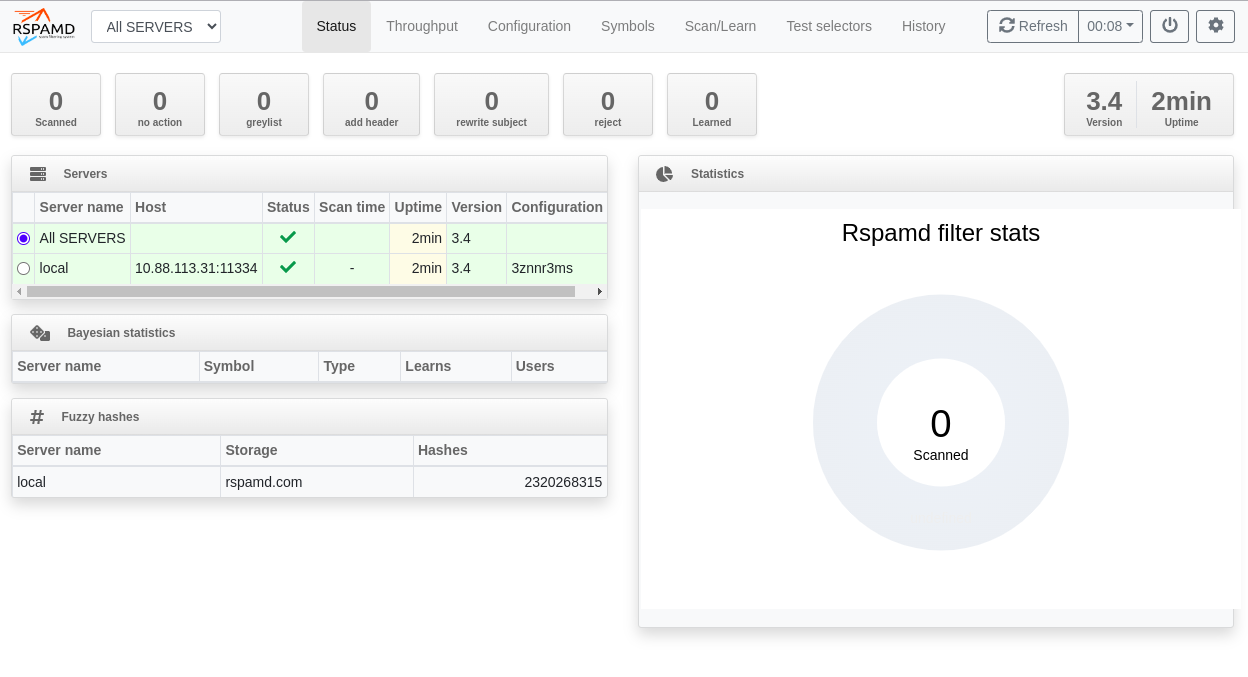
| + | *http://IP-Mailserver:11334 | ||
| + | [[Datei:Rspamd-1.png]] | ||
| + | =Milters= | ||
| + | *Milters sind Mail-Filter, die über das Milter-Protokoll mit MTA-Software wie Postfix oder Sendmail kommunizieren. | ||
| + | *Sie ermöglichen die Verarbeitung und Filterung von E-Mails in Echtzeit, bevor sie zugestellt werden. | ||
| + | *Milter werden häufig für Spam-Filterung, Virenscans und Inhaltsüberprüfungen eingesetzt. | ||
| + | =Einbinden in Postfix= | ||
| + | *postconf -e "smtpd_milters=inet:127.0.0.1:11332" | ||
| + | *postconf -e "non_smtpd_milters=inet:127.0.0.1:11332" | ||
| + | *postfix reload | ||
| + | =Gtube Testmail= | ||
| + | *echo 'XJS*C4JDBQADN1.NSBN3*2IDNEN*GTUBE-STANDARD-ANTI-UBE-TEST-EMAIL*C.34X' | mail -s "Boese Mail" martha | ||
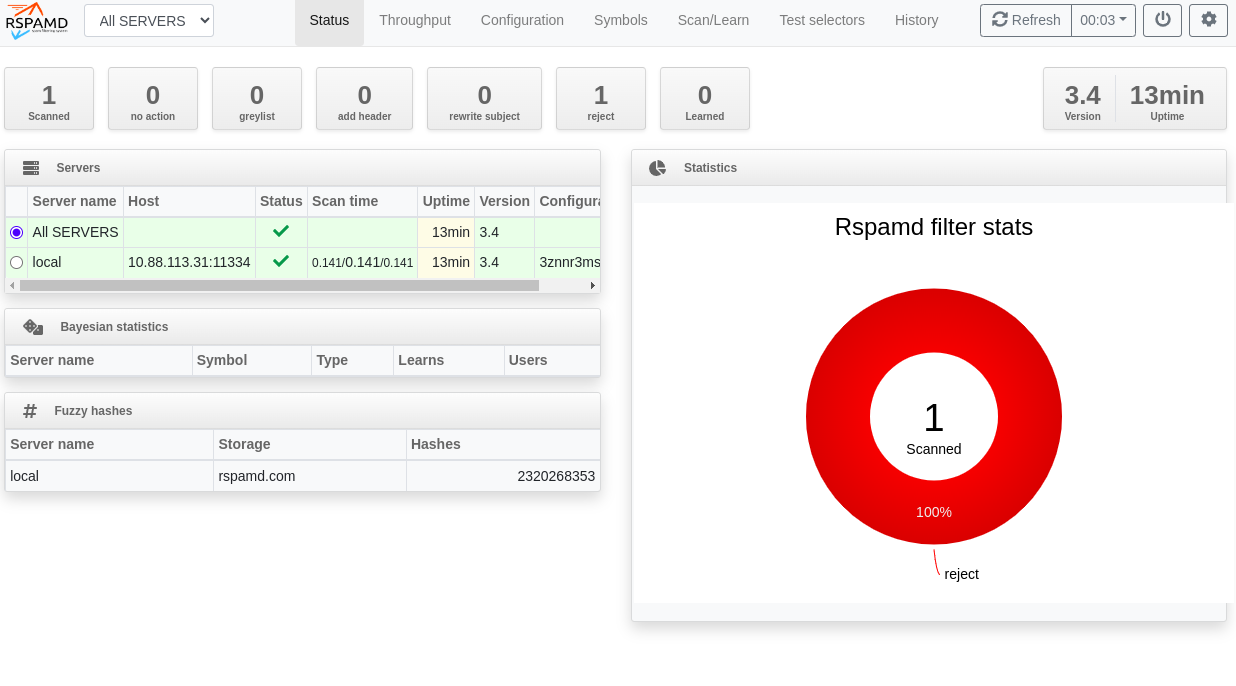
| + | =Resultat= | ||
| + | [[Datei:Rspamd-2.png]] | ||
| + | =Die Logs= | ||
| + | *journalctl -u postfix@-.service | grep cleanup | ||
| + | Mar 18 19:21:22 mail.it113.int postfix/cleanup[7407]: 88BDDE0792: milter-reject: END-OF-MESSAGE from localhost[127.0.0.1]: 5.7.1 Gtube pattern; from=<root@mail.it113.int> to=<martha@mail.it113.int> | ||
| + | Mar 18 19:21:22 mail.it113.int postfix/cleanup[7407]: 88BDDE0792: to=<martha@mail.it113.int>, orig_to=<martha>, relay=none, delay=0.19, delays=0.19/0/0/0, dsn=5.7.1, status=bounced (Gtube pattern) | ||
| + | Mar 18 19:21:22 mail.it113.int postfix/cleanup[7410]: B3D24E07C2: message-id=<20250318182122.B3D24E07C2@mail.it113.int> | ||
| + | =Restart= | ||
| + | *systemctl restart rspamd | ||
| + | =RBL-Integration in Rspamd und Postfix (Proof of Concept)= | ||
| + | ==Rspamd mit lokaler RBL== | ||
| + | ===Configuration=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *vi /etc/rspamd/local.d/multimap.conf | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | blacklist_ip { | ||
| + | type = "ip"; | ||
| + | map = "/etc/rspamd/local.d/local_rbl.txt"; | ||
| + | symbol = "LOCAL_RBL_HIT"; | ||
| + | action = "reject"; | ||
| + | description = "Lokale RBL-Hit"; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | ===Blackliste=== | ||
| + | *echo 10.88.113.21 > /etc/rspamd/local.d/local_rbl.txt | ||
| + | ===Rspamd neustarten=== | ||
| + | *systemctl restart rspamd | ||
| + | ===Tests=== | ||
| + | ;postiv | ||
| + | *echo hallo welt | rspamc -i 10.88.113.22 | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | Results for file: stdin (0 seconds) | ||
| + | [Metric: default] | ||
| + | Action: add header | ||
| + | Spam: true | ||
| + | Score: 7.90 / 15.00 | ||
| + | Symbol: ARC_NA (0.00) | ||
| + | Symbol: MIME_GOOD (-0.10)[text/plain] | ||
| + | Symbol: MIME_TRACE (0.00)[0:+] | ||
| + | Symbol: MISSING_DATE (1.00) | ||
| + | Symbol: MISSING_FROM (2.00) | ||
| + | Symbol: MISSING_MID (2.50) | ||
| + | Symbol: MISSING_SUBJECT (0.50) | ||
| + | Symbol: MISSING_TO (2.00) | ||
| + | Symbol: RCVD_COUNT_ZERO (0.00)[0] | ||
| + | Message-ID: undef | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | ;negativ | ||
| + | *echo hallo welt | rspamc -i 10.88.113.21 | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | Results for file: stdin (0 seconds) | ||
| + | [Metric: default] | ||
| + | Action: reject | ||
| + | Spam: true | ||
| + | Score: -0.10 / 15.00 | ||
| + | Symbol: ARC_NA (0.00) | ||
| + | Symbol: LOCAL_RBL_HIT (0.00)[10.88.113.21] | ||
| + | Symbol: MIME_GOOD (-0.10)[text/plain] | ||
| + | Symbol: MIME_TRACE (0.00)[0:+] | ||
| + | Message-ID: undef | ||
| + | Message - smtp_message: Matched map: LOCAL_RBL_HIT | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Clamav einbinden= | ||
| + | ==== Aktivierung von ClamAV in Rspamd Muss noch getestet werden==== | ||
| + | *[[clamav-chatgpt]] | ||
| + | *[[clamav-ngrok]] | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 20. März 2025, 18:31 Uhr
Rspamd und ClamAV installieren
Debian/Ubuntu
- apt install rspamd clamav-daemon clamav-freshclam redis
RHEL/CentOS
- dnf install rspamd clamav clamav-update redis
Enablen und Startend er Dienste
- systemctl enable rspamd --now
- systemctl enable clamav-daemon --now
- systemctl start redis
- systemctl enable redis.service
Läuft alles
- systemctl status rspamd
- systemctl status clamav-daemon
- systemctl status redis
Dienste und Ports von Rspamd
Rspamd Proxy
- Der Rspamd Proxy dient als Eingangsfilter für E-Mails und leitet sie an die entsprechenden Worker weiter, um die Last zu verteilen.
Port: 11332/tcp (Standardport für Proxy-Dienste)
Rspamd Worker
- Der Rspamd Worker führt die eigentliche Spam-Analyse durch und verarbeitet eingehende Nachrichten anhand von Regeln, Statistiken und externen Diensten.
Port: 11333/tcp (Standardport für Worker-Dienste)
Rspamd Controller
- Der Rspamd Controller stellt eine API für Konfiguration, Statistiken und manuelles Training des Filters zur Verfügung.
Port: 11334/tcp (Standardport für den Controller)
Passwort für den Rspamd Controller und Port nach aussen öffen
- Passwort erzeugen
- rspamadm pw
Enter passphrase: $2$mqbbp8yb4fz8febgpxk7rb4db9p5njwg$xior3gxjbuc76bhsq4rapq7x98cssrm9qkr49kwapgdsahmpzjny
- In der Worker Datei eintragen
- Port an allen Interfaces lauschen lassen
- cat /etc/rspamd/override.d/worker-controller.inc
password = "$2$mqbbp8yb4fz8febgpxk7rb4db9p5njwg$xior3gxjbuc76bhsq4rapq7x98cssrm9qkr49kwapgdsahmpzjny"; bind_socket ="*:11334";
Restart
- systemctl restart rspamd
Zugriff auf das Webinterface
Milters
- Milters sind Mail-Filter, die über das Milter-Protokoll mit MTA-Software wie Postfix oder Sendmail kommunizieren.
- Sie ermöglichen die Verarbeitung und Filterung von E-Mails in Echtzeit, bevor sie zugestellt werden.
- Milter werden häufig für Spam-Filterung, Virenscans und Inhaltsüberprüfungen eingesetzt.
Einbinden in Postfix
- postconf -e "smtpd_milters=inet:127.0.0.1:11332"
- postconf -e "non_smtpd_milters=inet:127.0.0.1:11332"
- postfix reload
Gtube Testmail
- echo 'XJS*C4JDBQADN1.NSBN3*2IDNEN*GTUBE-STANDARD-ANTI-UBE-TEST-EMAIL*C.34X' | mail -s "Boese Mail" martha
Resultat
Die Logs
- journalctl -u postfix@-.service | grep cleanup
Mar 18 19:21:22 mail.it113.int postfix/cleanup[7407]: 88BDDE0792: milter-reject: END-OF-MESSAGE from localhost[127.0.0.1]: 5.7.1 Gtube pattern; from=<root@mail.it113.int> to=<martha@mail.it113.int> Mar 18 19:21:22 mail.it113.int postfix/cleanup[7407]: 88BDDE0792: to=<martha@mail.it113.int>, orig_to=<martha>, relay=none, delay=0.19, delays=0.19/0/0/0, dsn=5.7.1, status=bounced (Gtube pattern) Mar 18 19:21:22 mail.it113.int postfix/cleanup[7410]: B3D24E07C2: message-id=<20250318182122.B3D24E07C2@mail.it113.int>
Restart
- systemctl restart rspamd
RBL-Integration in Rspamd und Postfix (Proof of Concept)
Rspamd mit lokaler RBL
Configuration
- vi /etc/rspamd/local.d/multimap.conf
blacklist_ip {
type = "ip";
map = "/etc/rspamd/local.d/local_rbl.txt";
symbol = "LOCAL_RBL_HIT";
action = "reject";
description = "Lokale RBL-Hit";
}
Blackliste
- echo 10.88.113.21 > /etc/rspamd/local.d/local_rbl.txt
Rspamd neustarten
- systemctl restart rspamd
Tests
- postiv
- echo hallo welt | rspamc -i 10.88.113.22
Results for file: stdin (0 seconds) [Metric: default] Action: add header Spam: true Score: 7.90 / 15.00 Symbol: ARC_NA (0.00) Symbol: MIME_GOOD (-0.10)[text/plain] Symbol: MIME_TRACE (0.00)[0:+] Symbol: MISSING_DATE (1.00) Symbol: MISSING_FROM (2.00) Symbol: MISSING_MID (2.50) Symbol: MISSING_SUBJECT (0.50) Symbol: MISSING_TO (2.00) Symbol: RCVD_COUNT_ZERO (0.00)[0] Message-ID: undef
- negativ
- echo hallo welt | rspamc -i 10.88.113.21
Results for file: stdin (0 seconds) [Metric: default] Action: reject Spam: true Score: -0.10 / 15.00 Symbol: ARC_NA (0.00) Symbol: LOCAL_RBL_HIT (0.00)[10.88.113.21] Symbol: MIME_GOOD (-0.10)[text/plain] Symbol: MIME_TRACE (0.00)[0:+] Message-ID: undef Message - smtp_message: Matched map: LOCAL_RBL_HIT