Suricata IPS: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Zur Navigation springen
Zur Suche springen
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| − | *[[Suricata IPS iptables]] | + | =Grundlagen und Installation= |
| + | *[[Suricata Grundlagen]] | ||
| + | *[[Suricata Installation]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Versuchsaufbau= | ||
| + | {{#drawio:ips-netz}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | =IPS= | ||
| + | *Wir können mit iptables Pakete abfangen und einer QUEUE übergeben | ||
| + | *Diese QUEUE wird von suricata gelesen und ihrem REGELWERK übergeben. | ||
| + | *Wenn das Paket mit einer Regel übereinstimmt, wird eine Aktion ausgelöst. | ||
| + | *Alert führt zu einer Meldung | ||
| + | *Bei Drop wird das Paket verworfen. | ||
| + | {{#drawio:ips}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Konfiguration Suricata = | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''vim /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml''' | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | %YAML 1.1 | ||
| + | --- | ||
| + | # Variablen für die Adressgruppen festlegen | ||
| + | vars: | ||
| + | address-groups: | ||
| + | LAN: "[192.168.10.0/24]" | ||
| + | DMZ: "[172.18.10.0/24]" | ||
| + | INT: "[$LAN,$DMZ]" | ||
| + | EXTERNAL_NET: "!$INT" | ||
| + | |||
| + | #Suricate nimmt die Pakete von Iptables wieder auf | ||
| + | nfq: | ||
| + | mode: repeat | ||
| + | repeat-mark: 1 | ||
| + | repeat-mask: 1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | # Standard-Log-Verzeichnis | ||
| + | default-log-dir: /var/log/suricata/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Statistiken aktivieren | ||
| + | stats: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | interval: 8 | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Ausgaben konfigurieren | ||
| + | outputs: | ||
| + | - fast: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | filename: fast.log | ||
| + | append: yes | ||
| + | - alert-debug: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | filename: alert-debug.log | ||
| + | append: yes | ||
| + | - stats: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | filename: stats.log | ||
| + | append: yes | ||
| + | totals: yes | ||
| + | threads: no | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Logging-Einstellungen | ||
| + | logging: | ||
| + | default-log-level: notice | ||
| + | outputs: | ||
| + | - console: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | - file: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | level: info | ||
| + | filename: suricata.log | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Netzwerkschnittstellen konfigurieren | ||
| + | af-packet: | ||
| + | - interface: enp0s3 | ||
| + | threads: auto | ||
| + | cluster-id: 97 | ||
| + | cluster-type: cluster_flow | ||
| + | defrag: yes | ||
| + | - interface: enp0s8 | ||
| + | threads: auto | ||
| + | cluster-id: 98 | ||
| + | cluster-type: cluster_flow | ||
| + | defrag: yes | ||
| + | - interface: enp0s9 | ||
| + | threads: auto | ||
| + | cluster-id: 99 | ||
| + | cluster-type: cluster_flow | ||
| + | defrag: yes | ||
| + | |||
| + | # PID-Datei | ||
| + | pid-file: /var/run/suricata.pid | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Coredump-Einstellungen | ||
| + | coredump: | ||
| + | max-dump: unlimited | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Host-Modus | ||
| + | host-mode: auto | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Unix-Befehlseingabe konfigurieren | ||
| + | unix-command: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | filename: /var/run/suricata-command.socket | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Engine-Analyse-Einstellungen | ||
| + | engine-analysis: | ||
| + | rules-fast-pattern: yes | ||
| + | rules: yes | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Defragmentierungseinstellungen | ||
| + | defrag: | ||
| + | memcap: 32mb | ||
| + | hash-size: 65536 | ||
| + | trackers: 65535 | ||
| + | max-frags: 65535 | ||
| + | prealloc: yes | ||
| + | timeout: 60 | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Standardregelverzeichnis | ||
| + | default-rule-path: /etc/suricata/rules | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Regel-Dateien | ||
| + | rule-files: | ||
| + | - local.rules | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Klassifikationsdatei | ||
| + | classification-file: /etc/suricata/classification.config | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Referenzkonfigurationsdatei | ||
| + | reference-config-file: /etc/suricata/reference.config | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | # Referenzkonfigurationsdatei | ||
| + | reference-config-file: /etc/suricata/reference.config | ||
| + | app-layer: | ||
| + | protocols: | ||
| + | http: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | tls: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | dcerpc: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | smb: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | ftp: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | ssh: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | smtp: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | dns: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | modbus: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | enip: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | dnp3: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | nfs: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | ntp: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | tftp: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | ikev2: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | krb5: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | dhcp: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | snmp: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | sip: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | rfb: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | mqtt: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | rdp: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | http2: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | imap: | ||
| + | enabled: yes | ||
| + | |||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Local Rules = | ||
| + | |||
| + | *cat /etc/suricata/rules/local.rules | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | alert icmp any any -> any any (msg:"ICMP Test"; flow:to_server; sid:1;) | ||
| + | drop http any any -> any any (msg: "SQL Injection Attempt!"; flow:established,to_server; http.request_body; content: "OR 1=1"; sid:2;) | ||
| + | drop dns any any -> any any (msg:"Kein Googlen"; dns.query; content:"google"; nocase; sid:3;) | ||
| + | drop http any any -> any any (msg: "Possible SQL Injection attack (Contains singlequote POST DATA)"; flow:established,to_server; content:"%27"; nocase; http_client_body; sid:4;) | ||
| + | drop http any any -> any any (msg: "Possible Command Injection attack (Contains semicolon POST DATA)"; flow:established,to_server; content:"%3B"; nocase; http_client_body; sid:5;) | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Firewallanpassung = | ||
| + | |||
| + | = NFQUEUE Repeat = | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Damit Suricata die nicht gedroppten Pakete automatisch akzeptiert, sondern dies der Firewall überlässt, kann es diese Pakete markieren und zurück zu iptables schicken | ||
| + | * Markierungen folgen der Syntax $''MARK''/$'''MASK''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | == iptables Version == | ||
| + | * '''vim /usr/local/sbin/firewall''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | iptables -P FORWARD DROP | ||
| + | iptables -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT | ||
| + | iptables -A FORWARD -m mark ! --mark ''1''/'''1''' -j NFQUEUE | ||
| + | iptables -A FORWARD -j LOG --log-prefix "iptables return from Suricata: " | ||
| + | # Hier geht es mit den normalen Regeln weiter | ||
| + | |||
| + | == nftables Version == | ||
| + | * '''vim /etc/nftables.conf''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="nftables"> | ||
| + | table inet filter { | ||
| + | chain forward { | ||
| + | type filter hook forward priority 0; policy drop; | ||
| + | ct state established,related accept | ||
| + | # An Suricata übergeben, wenn Mark-Bit 0 nicht gesetzt | ||
| + | meta mark and 1 != 1 queue | ||
| + | # Logging und Akzeptanz nach Rückgabe durch Suricata (mit gesetztem Mark) | ||
| + | log prefix "nftables return from Suricata: " | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | # Hier geht es mit den normalen Regeln weiter | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Suricata Anpassung == | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | nfq: | ||
| + | mode: repeat | ||
| + | repeat-mark: ''1'' | ||
| + | repeat-mask: '''1''' | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | ==Start suricata== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''suricata -D -q 0''' | ||
| + | * Den Unterschied zwischen ''repeat'' und ''accept'' kann man mit Ping und SSH testen (falls SSH in der FORWARD Kette blockiert ist) | ||
| + | * Die Verstöße können folgendermaßen gesehen werden | ||
| + | *'''tail -fn0 ''/var/log/suricata/fast.log'' ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Ersatz des IDS durch IPS = | ||
| + | * Die Standard ''.service''-Datei der Debian Installation stellt Suricata in den IDS-Modus | ||
| + | * Für den Start des IPS-Modus über systemd muss eine eigene ''.service''-Datei geschrieben werden | ||
| + | * '''cp ''/lib/systemd/system/suricata.service'' ''suricata-ips.service'' ''' | ||
| + | * '''vim ''suricata-ips.service'' ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [Unit] | ||
| + | Description=Suricata IDS/IDP daemon | ||
| + | After=network.target network-online.target | ||
| + | Requires=network-online.target | ||
| + | Documentation=man:suricata(8) man:suricatasc(8) | ||
| + | Documentation=https://suricata-ids.org/docs/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | [Service] | ||
| + | Type=forking | ||
| + | #Environment=LD_PRELOAD=/usr/lib/libtcmalloc_minimal.so.4 | ||
| + | PIDFile=/run/suricata.pid | ||
| + | ExecStart=/usr/bin/suricata -D -q 0 -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml --pidfile /run/suricata.pid | ||
| + | ExecReload=/usr/bin/suricatasc -c reload-rules ; /bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID | ||
| + | ExecStop=/usr/bin/suricatasc -c shutdown | ||
| + | Restart=on-failure | ||
| + | ProtectSystem=full | ||
| + | ProtectHome=true | ||
| + | |||
| + | [Install] | ||
| + | WantedBy=multi-user.target | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''cp ''suricata-ips.service'' ''/etc/systemd/system'' ''' | ||
| + | * Wechsel der zu verwendeten ''.service''-Datei | ||
| + | * '''systemctl disable --now suricata.service''' | ||
| + | * '''systemctl enable --now suricata-ips.service''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Links = | ||
| + | |||
| + | * https://docs.suricata.io/en/suricata-6.0.0/configuration/suricata-yaml.html#nfq | ||
| + | * https://medium.com/@mshulkhan/detection-attack-using-suricata-2-d93d423a435 | ||
Version vom 23. April 2025, 05:38 Uhr
Grundlagen und Installation
Versuchsaufbau
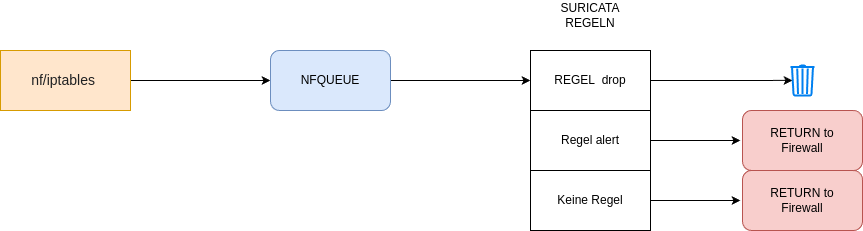
IPS
- Wir können mit iptables Pakete abfangen und einer QUEUE übergeben
- Diese QUEUE wird von suricata gelesen und ihrem REGELWERK übergeben.
- Wenn das Paket mit einer Regel übereinstimmt, wird eine Aktion ausgelöst.
- Alert führt zu einer Meldung
- Bei Drop wird das Paket verworfen.
Konfiguration Suricata
- vim /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml
%YAML 1.1
---
# Variablen für die Adressgruppen festlegen
vars:
address-groups:
LAN: "[192.168.10.0/24]"
DMZ: "[172.18.10.0/24]"
INT: "[$LAN,$DMZ]"
EXTERNAL_NET: "!$INT"
#Suricate nimmt die Pakete von Iptables wieder auf
nfq:
mode: repeat
repeat-mark: 1
repeat-mask: 1
# Standard-Log-Verzeichnis
default-log-dir: /var/log/suricata/
# Statistiken aktivieren
stats:
enabled: yes
interval: 8
# Ausgaben konfigurieren
outputs:
- fast:
enabled: yes
filename: fast.log
append: yes
- alert-debug:
enabled: yes
filename: alert-debug.log
append: yes
- stats:
enabled: yes
filename: stats.log
append: yes
totals: yes
threads: no
# Logging-Einstellungen
logging:
default-log-level: notice
outputs:
- console:
enabled: yes
- file:
enabled: yes
level: info
filename: suricata.log
# Netzwerkschnittstellen konfigurieren
af-packet:
- interface: enp0s3
threads: auto
cluster-id: 97
cluster-type: cluster_flow
defrag: yes
- interface: enp0s8
threads: auto
cluster-id: 98
cluster-type: cluster_flow
defrag: yes
- interface: enp0s9
threads: auto
cluster-id: 99
cluster-type: cluster_flow
defrag: yes
# PID-Datei
pid-file: /var/run/suricata.pid
# Coredump-Einstellungen
coredump:
max-dump: unlimited
# Host-Modus
host-mode: auto
# Unix-Befehlseingabe konfigurieren
unix-command:
enabled: yes
filename: /var/run/suricata-command.socket
# Engine-Analyse-Einstellungen
engine-analysis:
rules-fast-pattern: yes
rules: yes
# Defragmentierungseinstellungen
defrag:
memcap: 32mb
hash-size: 65536
trackers: 65535
max-frags: 65535
prealloc: yes
timeout: 60
# Standardregelverzeichnis
default-rule-path: /etc/suricata/rules
# Regel-Dateien
rule-files:
- local.rules
# Klassifikationsdatei
classification-file: /etc/suricata/classification.config
# Referenzkonfigurationsdatei
reference-config-file: /etc/suricata/reference.config
# Referenzkonfigurationsdatei
reference-config-file: /etc/suricata/reference.config
app-layer:
protocols:
http:
enabled: yes
tls:
enabled: yes
dcerpc:
enabled: yes
smb:
enabled: yes
ftp:
enabled: yes
ssh:
enabled: yes
smtp:
enabled: yes
dns:
enabled: yes
modbus:
enabled: yes
enip:
enabled: yes
dnp3:
enabled: yes
nfs:
enabled: yes
ntp:
enabled: yes
tftp:
enabled: yes
ikev2:
enabled: yes
krb5:
enabled: yes
dhcp:
enabled: yes
snmp:
enabled: yes
sip:
enabled: yes
rfb:
enabled: yes
mqtt:
enabled: yes
rdp:
enabled: yes
http2:
enabled: yes
imap:
enabled: yes
Local Rules
- cat /etc/suricata/rules/local.rules
alert icmp any any -> any any (msg:"ICMP Test"; flow:to_server; sid:1;) drop http any any -> any any (msg: "SQL Injection Attempt!"; flow:established,to_server; http.request_body; content: "OR 1=1"; sid:2;) drop dns any any -> any any (msg:"Kein Googlen"; dns.query; content:"google"; nocase; sid:3;) drop http any any -> any any (msg: "Possible SQL Injection attack (Contains singlequote POST DATA)"; flow:established,to_server; content:"%27"; nocase; http_client_body; sid:4;) drop http any any -> any any (msg: "Possible Command Injection attack (Contains semicolon POST DATA)"; flow:established,to_server; content:"%3B"; nocase; http_client_body; sid:5;)
Firewallanpassung
NFQUEUE Repeat
- Damit Suricata die nicht gedroppten Pakete automatisch akzeptiert, sondern dies der Firewall überlässt, kann es diese Pakete markieren und zurück zu iptables schicken
- Markierungen folgen der Syntax $MARK/$MASK
iptables Version
- vim /usr/local/sbin/firewall
iptables -P FORWARD DROP iptables -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -m mark ! --mark 1/1 -j NFQUEUE iptables -A FORWARD -j LOG --log-prefix "iptables return from Suricata: " # Hier geht es mit den normalen Regeln weiter
nftables Version
- vim /etc/nftables.conf
table inet filter {
chain forward {
type filter hook forward priority 0; policy drop;
ct state established,related accept
# An Suricata übergeben, wenn Mark-Bit 0 nicht gesetzt
meta mark and 1 != 1 queue
# Logging und Akzeptanz nach Rückgabe durch Suricata (mit gesetztem Mark)
log prefix "nftables return from Suricata: "
...
# Hier geht es mit den normalen Regeln weiter
}
}Suricata Anpassung
... nfq: mode: repeat repeat-mark: 1 repeat-mask: 1 ...
Start suricata
- suricata -D -q 0
- Den Unterschied zwischen repeat und accept kann man mit Ping und SSH testen (falls SSH in der FORWARD Kette blockiert ist)
- Die Verstöße können folgendermaßen gesehen werden
- tail -fn0 /var/log/suricata/fast.log
Ersatz des IDS durch IPS
- Die Standard .service-Datei der Debian Installation stellt Suricata in den IDS-Modus
- Für den Start des IPS-Modus über systemd muss eine eigene .service-Datei geschrieben werden
- cp /lib/systemd/system/suricata.service suricata-ips.service
- vim suricata-ips.service
[Unit] Description=Suricata IDS/IDP daemon After=network.target network-online.target Requires=network-online.target Documentation=man:suricata(8) man:suricatasc(8) Documentation=https://suricata-ids.org/docs/ [Service] Type=forking #Environment=LD_PRELOAD=/usr/lib/libtcmalloc_minimal.so.4 PIDFile=/run/suricata.pid ExecStart=/usr/bin/suricata -D -q 0 -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml --pidfile /run/suricata.pid ExecReload=/usr/bin/suricatasc -c reload-rules ; /bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID ExecStop=/usr/bin/suricatasc -c shutdown Restart=on-failure ProtectSystem=full ProtectHome=true [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
- cp suricata-ips.service /etc/systemd/system
- Wechsel der zu verwendeten .service-Datei
- systemctl disable --now suricata.service
- systemctl enable --now suricata-ips.service