TCP/IP vs. ISO/OSI: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Zur Navigation springen
Zur Suche springen
| Zeile 14: | Zeile 14: | ||
| rowspan="3" | Anwendung | | rowspan="3" | Anwendung | ||
| rowspan="3" | Daten | | rowspan="3" | Daten | ||
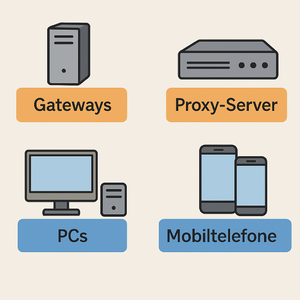
| − | | rowspan="4" | | + | | rowspan="4" | [[Datei:Devices-7.png|300px]] |
| − | [[Datei:Devices-7.png|300px]] | ||
| rowspan="3" | DNS, FTP, SNMP, DHCP, SSH, SMTP, POP3, LDAP, SMB, SSL, TLS, NetBIOS, HTTPS, HTTP, FTP, NFS, NTP, Telnet, IMAP, AFP, RPC, SMB | | rowspan="3" | DNS, FTP, SNMP, DHCP, SSH, SMTP, POP3, LDAP, SMB, SSL, TLS, NetBIOS, HTTPS, HTTP, FTP, NFS, NTP, Telnet, IMAP, AFP, RPC, SMB | ||
|- style="background-color:#fff0e6" | |- style="background-color:#fff0e6" | ||
| Zeile 42: | Zeile 41: | ||
| Internet | | Internet | ||
| Paket | | Paket | ||
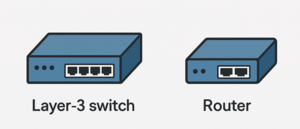
| − | | | + | |[[Datei:Devices-4.png|300px]] |
| − | [[Datei:Devices-4.png|300px]] | ||
| ICMP, IGMP, IP, IPsec, NAT | | ICMP, IGMP, IP, IPsec, NAT | ||
|- style="background-color:#f0e6ff" | |- style="background-color:#f0e6ff" | ||
| Zeile 52: | Zeile 50: | ||
| rowspan="2" | Netzwerkzugriffs- oder Sicherungsschicht | | rowspan="2" | Netzwerkzugriffs- oder Sicherungsschicht | ||
| rowspan="2" | Frame / Bits | | rowspan="2" | Frame / Bits | ||
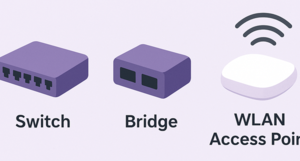
| − | | | + | |[[Datei:Devices-2.png|300px]] |
| − | [[Datei:Devices-2.png|300px]] | ||
| rowspan="2" | ARP, Ethernet, Token Ring, PPP, ATM, SLIP, 802.11, Frame Relay, MAC, LLDP, VLAN, Bluetooth, ISDN, L2TP, DSL, VTP | | rowspan="2" | ARP, Ethernet, Token Ring, PPP, ATM, SLIP, 802.11, Frame Relay, MAC, LLDP, VLAN, Bluetooth, ISDN, L2TP, DSL, VTP | ||
|- style="background-color:#f0f0f0" | |- style="background-color:#f0f0f0" | ||
| Zeile 62: | Zeile 59: | ||
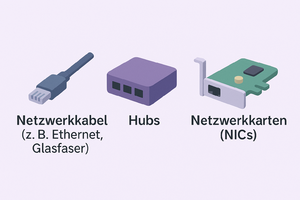
Zum Beispiel: Spannungspegel, maximale Übertragungsdistanzen, physikalische Anschlüsse usw. | Zum Beispiel: Spannungspegel, maximale Übertragungsdistanzen, physikalische Anschlüsse usw. | ||
Digitale Bits werden übertragen, um elektrische Signale für kabelgebundene Verbindungen und Funksignale für drahtlose Übertragung auf dieser Schicht umzuwandeln. | Digitale Bits werden übertragen, um elektrische Signale für kabelgebundene Verbindungen und Funksignale für drahtlose Übertragung auf dieser Schicht umzuwandeln. | ||
| − | | | + | |[[Datei:Devices-1.png|300px]] |
| − | [[Datei:Devices-1.png|300px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
[[Kategorie:Netzwerk]] | [[Kategorie:Netzwerk]] | ||